ADHESIVE BONDING/STAKING
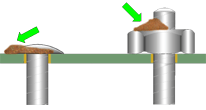
The primary purpose for adhesive bonding/staking is to protect and support components and parts that may be damaged by vibration, shock or handling. Bonding/staking material may either by resilient or rigid.
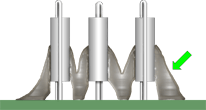
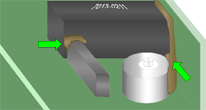
PREFERRED
ADHESIVE BONDING/STAKING
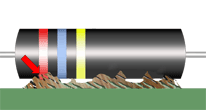
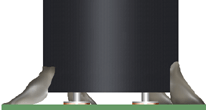
Adhesive bonding/staking material has been applied to the parts and locations specified by the approved engineering specification. Material quantity is sufficicnet to provide required support, but does not negate stress relief or mechanically compromise hardware reliability.
PREFERRED
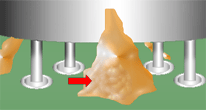
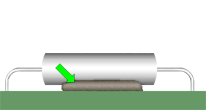
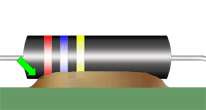
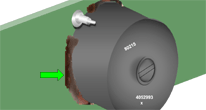
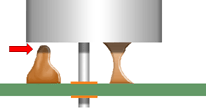
FLEXIBLE MATERIALS
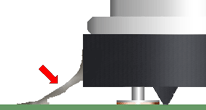
Flexible staking materials with a high thermal expansion coefficient shall not be applied where excessive stress may be damaging. As depicted, the staking material has been applied to the corners of the package.
NASA-STD-8739.1 [9.2.1]
PREFERRED
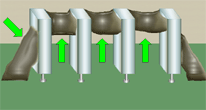
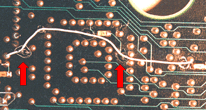
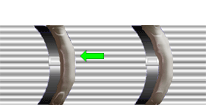
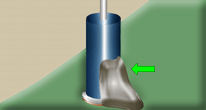
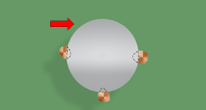
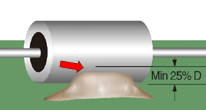
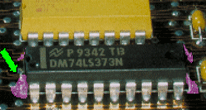
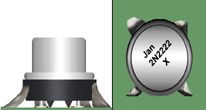
PERIPHERY RULE
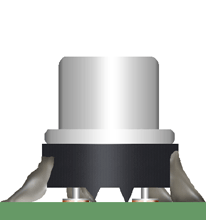
Staking material shall be of sufficient quantity to result in a minimum of 20% of the component's periphery being bonded.
Best Workmanship Practice
PREFERRED
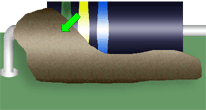
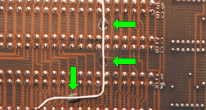
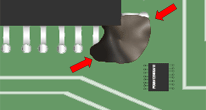
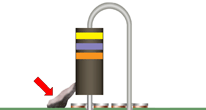
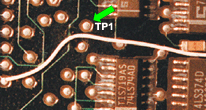
SOLDERABLE AREAS/TEST POINTS
Adhesive/staking material shall not be applied to areas that are to be soldered, or are to be used as test points. Contamination/solderability issue.
Best Workmanship Practice